Roof Pitch Guide • Roof Pitch Chart
By Jack Gray, Roof Online Editor • Last updated April 18, 2024
Table of Contents
- Roof Pitch Chart
- What is Roof Pitch?
- Low-Slope vs. Steep-Slope Roofs
- Why Roof Pitch is Important
- Roof Pitch Visualizer
- More Roof Pitch Articles and Tables
- Useful Roof Pitch Tools
- Roof Pitch Data Table
- More Roof Pitch Articles
Roof Pitch Chart
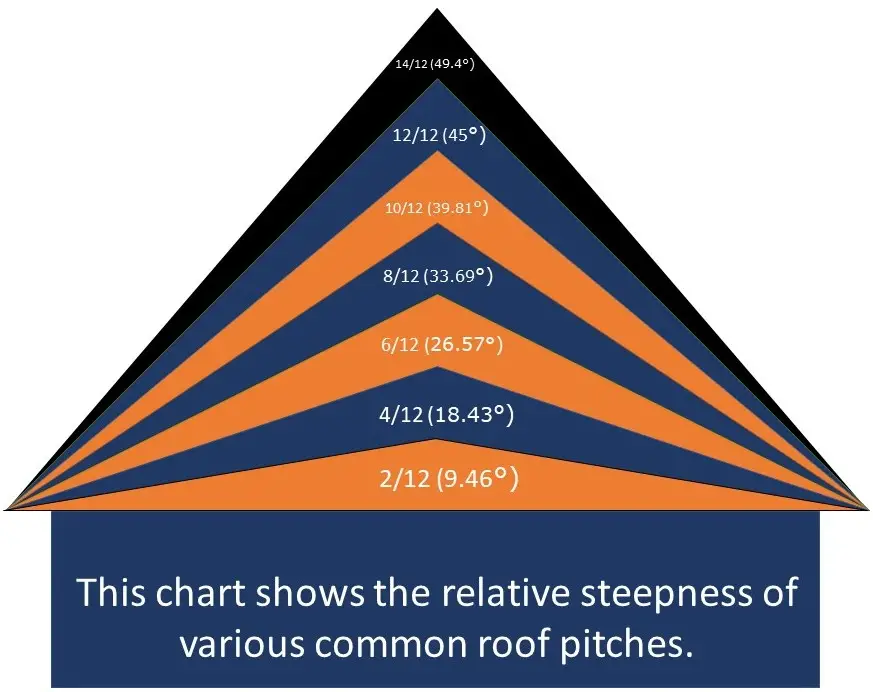
What is Roof Pitch?
Roof pitch is a mathematical expression of how steep your roof is. When using pitch (rather than degrees or percentage), the slope of the roof is given as a ratio of the vertical rise to the horizontal run (rise/run).
Traditionally, this expression of pitch takes the form “X:12″ or “X-in-12″, where X is the number of units (inches) of vertical rise of the roof and 12 inches is the run.
12 is always used for the run because there are 12 inches in a foot, and you are stating how many inches the roof rises over a one foot horizontal span.
Places that don’t use inches typically don’t use standard roof pitch, either. Instead, they express roof slope in degrees.
The steepness of a roof may be expressed in degrees or as a percentage (see Ways to Express Roof Slope: Pitch, Degrees, and Percentage).
Low-Slope vs. Steep-Slope Roofs
A low-slope roof is commonly called a “flat roof”, although building codes forbid perfectly flat roofs and require all flat roofs to have some slope. This requirement is intended to ensure that water will drain off the roof.
Perfectly flat roofs would be at a much higher risk of overloading and collapsing due to standing water.
A low-slope roof will typically have a pitch between ¼-in-12 and 2½-in-12. The technical definition of a low-slope roof is any roof having a slope of less than 3-in-12 (approximately 14 degrees above horizontal).
“Pitched” or “steep-slope” roofing refers to any roof with a slope of 3-in-12 or above (as defined and used in the technical literature of the roofing industry).
In the context of OSHA’s safety guidance, “steep roof means a roof having a slope greater than 4-in-12 (vertical to horizontal)”. (from OSHA’s Safety and Health Regulations for Construction, Section 1926.500(b)(2)).
More casually, roofers who specialize in pitched roofing will often use “steep slope” to refer to roofs with a 9/12 or greater pitch.
Low-slope roofs typically have membrane-style roof coverings and steep-slope roofs typically have shingles or tiles.
Because shingles and tiles can also sometimes be installed on roofs that have a pitch under 3-in-12 (as low as 2-in-12 if special underlayment requirements are met) there is often confusion about where the cut-off point is between low-slope and pitched roofs.
In all the technical literature, the cut-off point is 3-in-12. Any use of asphalt shingles, for example, on a roof with a pitch below 3-in-12 is considered a “low-slope application” of the shingles.
Generally, although there are exceptions (such as the case with asphalt shingles mentioned above), low-slope roofs will have a different fundamental method of waterproofing than pitched roofs.
Low-slope roofs may drain slowly and they depend on a continuous waterproof barrier to keep water out of the building, while pitched roofs depend on gravity and slope to get water off the roof as fast as possible while ensuring the water doesn’t flow up and underneath the shingles or tiles.
Low-slope roofs use a different set of materials, have different installation techniques, and have far different maintenance requirements than steep-slope roofs.
Why Roof Pitch is Important
- The pitch of a roof determines what roofing materials can be used on the roof (see Minimum Roof Pitch for Every Roofing Material).
- The pitch of a roof is an important factor in figuring out how much roofing material will be needed when installing a new roof, because it allows you to accurately calculate the surface area of the roof (see How to Find the Area of a Roof).
- The pitch of a roof is important when making certain roof drainage calculations (see Roof Drainage).
- The pitch of a roof determines the roof slope factor, also called the roof slope multiplier, which is used to calculate proper rafter length as well as roof area.
- The pitch of a roof determines the hip and valley factor, which is used to calculate the proper length of hip and valley rafters.
Roof Pitch Visualizer
We made this little tool in order to let people play around and get an idea of what just about any roof pitch looks like.
Roof Pitch Visualizer
More Roof Pitch Articles and Tables
See our Roof Pitch Multiplier Chart for a much longer list of roof slope factors, including slope factors for roof pitches by the half-inch. We also explain the math behind the multiplier.
See our Hip and Valley Factor Chart for a much longer list of hip and valley factors, including hip and valley factors for pitches by the half-inch. We also explain the math behind the factor.
Roof Pitch to Degrees • Degrees to Roof Pitch has conversion charts that convert slopes from 1 to 72 degrees into standard pitch and roof pitches from ⅛-in-12 to 36½-in-12 into degrees.
Minimum Required Roof Pitch for Every Roofing Material explains why you shouldn’t use a roofing material on a slope that is lower than recommended, and has a chart showing the minimum slopes required by the building code.
Useful Roof Pitch Tools
If you’re not sure what the slope of your roof is and you want to determine that in either degrees or standard roof pitch, we recommend this slope finder on Amazon. It’s very inexpensive and very accurate.
If you want to know the slope of anything to an amazing degree of accuracy and you like cool new tools, you should check out this digital level.
It may be way too expensive for what you need, but this is what professionals use. It will tell you the slope of your roof in degrees, rise/run, or percentage, and automatically convert from one to the other.
If you’re reading this article, you may want to look into getting yourself a construction calculator. This one is very good.
Roof Pitch Data Table
| Roof Pitch Information Table | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Pitch of Roof | Roof Slope in Degrees | Roof Slope Factor | Hip and Valley Factor |
| ¼:12 | 1.193° | 1.0002 | 1.4144 |
| ½:12 | 2.386° | 1.001 | 1.4148 |
| 1:12 | 4.76° | 1.003 | 1.4167 |
| 2:12 | 9.46° | 1.014 | 1.4240 |
| 3:12 | 14.04° | 1.031 | 1.4362 |
| 4:12 | 18.43° | 1.054 | 1.4529 |
| 5:12 | 22.62° | 1.083 | 1.4743 |
| 6:12 | 26.57° | 1.118 | 1.5 |
| 7:12 | 30.26° | 1.158 | 1.5298 |
| 8:12 | 33.69° | 1.202 | 1.5635 |
| 9:12 | 36.87° | 1.250 | 1.6008 |
| 10:12 | 39.81° | 1.302 | 1.6415 |
| 11:12 | 42.51° | 1.357 | 1.6853 |
| 12:12 | 45° | 1.414 | 1.7321 |
| 13:12 | 47.29° | 1.474 | 1.7815 |
| 14:12 | 49.4° | 1.537 | 1.8333 |
| 15:12 | 51.34° | 1.601 | 1.8874 |
| 16:12 | 53.13° | 1.667 | 1.9437 |
| 17:12 | 54.78° | 1.734 | 2.0017 |
| 18:12 | 56.31° | 1.803 | 2.0616 |